Shoulder Osteoarthritis:
Possible Causes :
Subjective Assessment :
The patient will complain of a stiff and painful shoulder
They may report a restriction In movement and hence difficulty with functional activities
Interruption of sleep and difficulty getting comfortable at night is common
The patient may report a ‘grinding’ , ‘grating’ or ‘clicking’ sensation in the shoulder
Objective Assessment :
Global restriction in movement
Stiffness on palpation of the glenohumeral joint
Active = passive range of movement
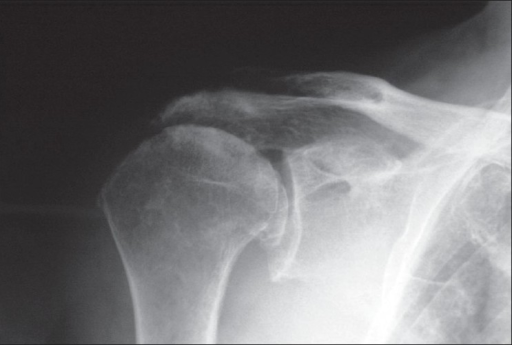
X-Ray evidence of osteoarthritis
References:
Image from OpenI – Licensed by CC
Treatment :
Refer to Physiotherapy for exercises and manual therapy to prevent any further stiffness and restriction in movement
Painkillers and anti-inflammatories
Steroid injections –may give short term relief to the patient, though period is unpredictable due to the wide variability of the disease
Surgery can be considered once the patient has completed 3 months of conservative management and Physiotherapy
Patients may initially be offered arthroscopic treatment but this is usually only a temporary measure before the patient eventually needs an arthroplasty
A shoulder replacement is indicated where there is severe, non-resolvable pain or previous failed treatment options
References:
Image from OpenI – Licensed by CC